Key Strategies to Improve Business Web Application Security
BY : Sdreatech
02-Feb-2024

Web Application Security?
Web application security is essential for online businesses. This is the concept of building websites to work properly even when attacked, which is also known as Web AppSec. Unfortunately, web apps are still a major source of cyberattacks and data leaks. Poor web apps might expose customer, payment, and other critical data. Injection attacks, cross-site scripting, and security issues occasionally target web programs.
In this article, we provide immediate web app security tips for developers and security teams.
Top web application risk
Technology and web applications are becoming more important in our daily lives; consequently, we must be aware of their risks. There are a variety of ever-changing risks to web apps, ranging from financial data theft to compromising personal information. In the current digital era, knowing these dangers is crucial for both developers and users.
So let's get started and investigate the top web application risks.

1. Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
The most frequent risk associated with online applications is cross-site scripting. It happens when a hacker inserts malicious code into a web application, giving them the ability to change the content of websites, steal user information, or send users to unsafe websites.
2. SQL Injection
SQL injection allows attackers to access sensitive database data by inserting SQL instructions into web application input fields. This may lead to data theft, manipulation, or database takeover.
3. Invalid Authentication
When user authentication is not done correctly, it can lead to vulnerabilities that hackers can take advantage of. This is known as broken authentication. This allows unauthorized access to user accounts, sensitive data, and the web application.
4. Direct Access to Unsafe Objects
when a program gives out a reference to an internal implementation object, it's called an unsafe direct object reference. Hackers can change IDs to steal information or do other bad things.
5. Security Misconfiguration
Web, application, and web application misconfiguration causes security issues. Its weak passwords, unused services, outdated software, and more make the online application open to attacks.
6. Poor transport layer protection
Transmission of sensitive data without encryption is poor transport layer protection. Attackers may use this to intercept and take credit card numbers, login passwords, and other private information.
7. Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF)
An attack known as cross-site request forgery occurs when a hacker deceives a user into sending an unauthorized request, which causes undesired actions to be carried out on an online application. This can cause data alteration, unauthorized transactions, etc.
8. Invalid data
The web application processes user input without validation, creating an unvalidated input vulnerability. This allows attackers to inject malicious code, steal data, or disrupt the application.
9. Cryptostore Insecurity
Cryptographic storage that fails to encrypt passwords or credit card numbers is called insecure. Thus, attackers can steal and misuse data.
10. Unsafe Deserialization
An attack that takes advantage of the code required to convert data formats is known to be unsafe deserialization. Remote code execution lets attackers control the web application and obtain sensitive data.
Important Tips for web application security
Web applications are the foundation of businesses in the modern digital age, giving clients an easy and effective way to communicate with businesses. Through the application of theseImportant tips, you can protect your company from possible damage while guaranteeing the security and confidence of your clients. Let's delve into web application security!
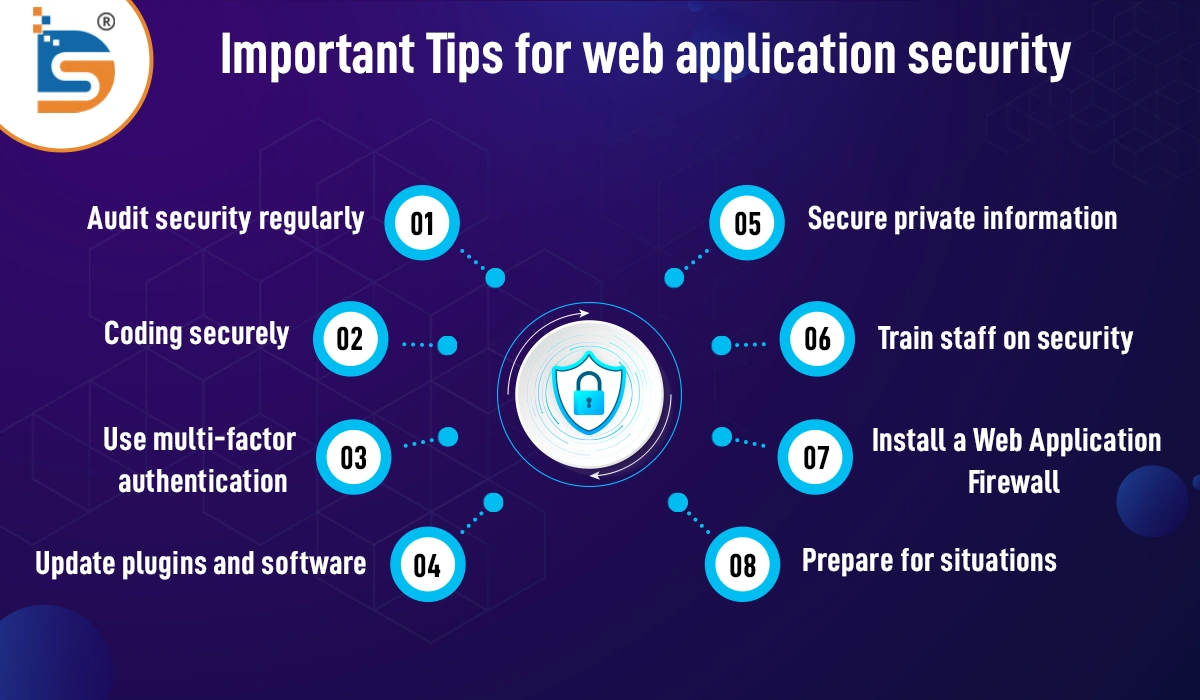
1. Audit security regularly
A security audit is a thorough examination of the security procedures and weaknesses in your web application. It helps find cybercriminal vulnerabilities. You can stay current on security threats and improve your application's security by conducting regular security audits.
2. Coding securely
Your web application may be vulnerable to assault if you use poor coding methods. Make sure your developers use input validation, output encoding, and error handling to avoid SQL injection and cross-site scripting.
3. Use multi-factor authentication
Using multiple forms of identity to access the app increases security with multi-factor authentication. This includes a password, fingerprint, SMS, or email one-time code. Even with a compromised password, it prevents unauthorized access to your app.
4. Update plugins and software
Due to recognized weaknesses, outdated software and plugins are accessible targets for hackers. Keeping your web application's software and plugins updated with security patches is critical. Avoid security breaches by checking for and installing updates.
5. Secure private information
To prevent unauthorized access, plain text data must be encrypted and transformed into code. Encrypting user data, passwords, and financial transactions in your web application is essential. A hacker can't read or utilize your information if they get access.
6. Train staff on security
In many companies, staff are the weakest link in security. The online application's security may be compromised by accidentally clicking on phishing scams or malicious links. In regular security training, you can teach personnel best practices and how to spot and report dangers.
7. Install a Web Application Firewall (WAF)
A WAF is an application- or hardware-based security solution that keeps an eye on and filters incoming web traffic. It can prevent SQL injections and cross-site scripting from reaching your web application.
8. Prepare for situations
Security breaches can happen despite all safeguards. To minimize damage and recover swiftly from an attack, an incident response strategy is essential. This plan should isolate the damaged system, inform authorities, and notify customers.
Conclusion
When compared to consumer-facing web apps, business apps are more vulnerable to security risks. As a result, security should not be seen as a legal requirement but as a strict and mission-critical task. Your company web app will be better protected if you follow the majority of these guidelines and procedures.